Certain things leave an impact on our minds for a very long duration of time. Do you remember the innovations and advertisements of a few popular brands like Oral B electric toothbrush, Kinder Joy, Uber eats, and many more?
I am sure you might remember them; all of them have emerged from creativity. These products and their advertisement have placed a deep mark on our memory to remember these companies. The major problem an organization or an entrepreneur face is to keep up with innovation to hold or improve their positions in their respective sectors. Innovation must be ingrained in the company’s culture; it cannot be a one-time event.
We are also aware of how difficult it may sometimes be to innovate.
And this is where Design Thinking enters into the picture.
But the question is can we design our thinking??? Is it possible to make innovations in our thinking?? How to think outside of that box?? I am sure these questions are very common, and each one who tries to innovate something undergoes these thought processes. Let us learn about “Design Thinking” and its importance.
Table of Contents
Design Thinking
Both the body of information generated about how individuals reason when presented with design issues and the collection of cognitive, strategic, and practical tactics that designers apply during the design process are meant to be understood under the umbrella term of “design thinking.”
Teams can employ design thinking, an iterative process that seeks to understand people, question preconceived notions, reframe problems, and generate novel, prototyped solutions before putting them to the test. Its five steps—Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test—are designed to help solve problems with unclear or incomplete parameters.

How Design Thinking is so Crucial?
Learning to recognize and adapt to users’ shifting contexts and habits is critical for anyone working in user experience (UX) design. The world has gotten more interconnected and complex since cognitive scientist and Nobel laureate Simon originally discussed design thinking in his 1969 book The Sciences of the Artificial and made several contributions to its tenets. After that, experts in sectors like design and engineering helped expand this extremely imaginative approach to meet the needs of contemporary humans.
In the twenty-first century, businesses across many sectors have found design thinking to be an effective tool for addressing issues faced by the people who use their goods and services. Because of its ability to reframe challenges in human-centric ways and focus on what’s most important to users, design thinking is very useful for tackling ill-defined/unknown difficulties (also known as wicked problems). Design thinking, as opposed to other design techniques, is almost unquestionably the most effective for “thinking outside the box.” With it, teams may do more effective user experience research, prototypes, and usability tests, which leads to the discovery of novel approaches to satisfying the requirements of end users.
Five-Step Process of Design Thinking
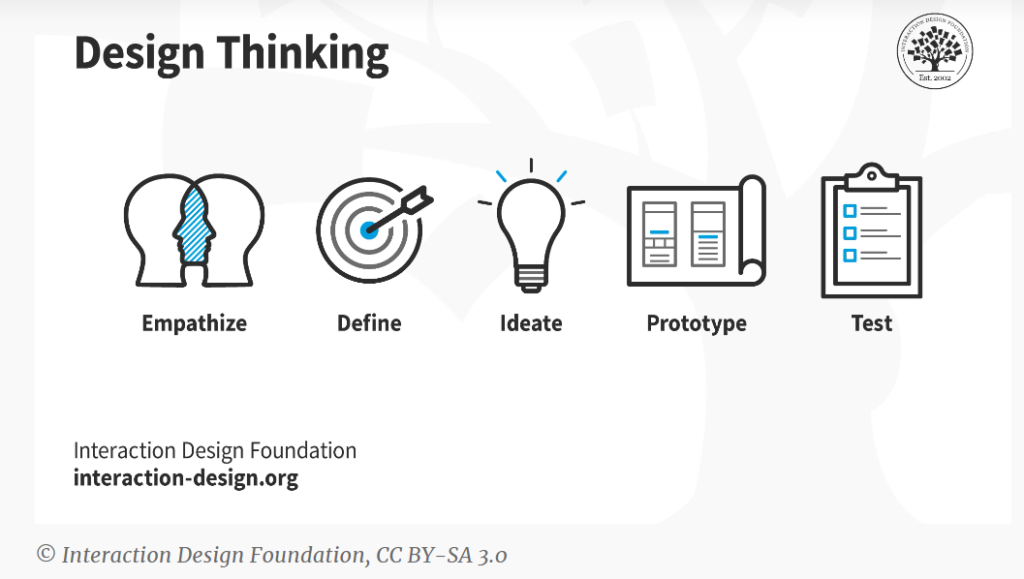
Empathize
At this stage, the designer watches how people use or react to a product or issue to learn how to improve it. The observations must be made with empathy, which means not passing judgment and not imposing ideas about what the consumer needs that you already know. When you observe with empathy, you can find out about problems that the customer didn’t know about or couldn’t express. Now it’s easier to understand the human need you’re building for.
Define
In the second step, you take what you learned in the first step and use it to define the problem you’re trying to solve. Think about the problems your customers often face and what you’ve learned from seeing how the problem affects them. Once you have put all of your findings together, you will be able to describe the problem they face.
Ideate
After identifying the issue, the following step is to brainstorm potential remedies. These sessions can take place in a group, where your team gets together in an office that encourages creativity and cooperation, or they can be done alone, in a space like an innovation lab. The key is to generate many different ideas. The procedure’s finish should provide you with some pointers for what to do next.
Prototype
At this point, abstract concepts are materialized into operable plans. We don’t expect prototypes to have all the bugs worked out. Developing a prototype is to see how customers react to an idea as soon as possible. Prototypes can be anything from a landing page to gauge consumer interest in a product to a film showcasing improved logistical processes.
Test
Customers’ reactions to a prototyped solution should be closely monitored. Feedback is gathered at this point.
Design thinking is an iterative approach as opposed to a linear one. After finishing the fifth stage, you will probably have to repeat one or more of the earlier stages. Perhaps the results of the testing convinced you to go back to the fourth step and make another prototype. Or it could show that your understanding of what the market needs is off. In this scenario, you need to start the procedure over from the beginning.
Trying to find out what skills fit your interests in this field? Speak with our Gyaannirudra’s expert career counsellor for personalized step-by-step advice on your career exploration journey.
Can you explain the benefits of using Design Thinking in the business world?

You, as a designer, play a crucial role in shaping the final products and customer experiences your company offers. By incorporating Develop Thinking into your approach, you may increase the likelihood that the products you create will be both profitable and environmentally friendly.
Thus, think about some of the most significant benefits of using Design Thinking on the job:
When paired with lean and agile methodologies, Design Thinking’s emphasis on problem-solving and identifying feasible solutions can significantly reduce design and development times.
Bringing profitable products to market quickly reduces expenses and increases returns on investment. Design Thinking has been proven to generate a sizable ROI; for instance, IBM Design Thinking teams have calculated an ROI of up to 300%.
Increases user engagement and loyalty over time. Design Thinking’s focus on the end-user improves both retention and loyalty.
Design Thinking fosters innovation and originality by questioning preconceived notions and long-held beliefs and encouraging all parties involved to think in novel ways. This results in a culture of innovation that permeates the entire company, not just the design department.
Fortunately, Design Thinking is not just for the design department; it can be applied throughout an organization. Facilitates communication amongst groups and makes use of group intelligence. Also, it applies to virtually any company team. Design Thinking can help you innovate, center your attention on the user, and ultimately create products that solve real problems for real people, whether you’re trying to establish a Design Thinking culture across your entire organization or just looking to improve your approach to user-centric design.
What benefits does design thinking provide to a business?
As a result of all the recent conversation about design thinking, “everyone who has a challenge that requires creative problem solving could benefit from this approach,” as Eppinger put it. As a result, managers may utilize it “any time they have a challenge, a problem to handle,” not simply while developing a new product or service.
Executives in various industries can benefit from applying design thinking to business difficulties. It can drive them to rethink their product lines, extend their markets, provide more value to clients, and innovate to preserve their competitive edge. “I don’t know any industries that can’t use design thinking,” says Eppinger.
Want to know more about “Design Thinking”? Please click on the link given below
Want to know more about the importance of Design Thinking in helping you grow through your entrepreneurial journey, Click here to Book your FREE Consultation Call with our Head Mentor
In case, if you feel that we have missed something important in this article and need to be included for its betterment, feel free to share your suggestions with us through comments or mail us at [email protected].
Stay connected with us to be aware of the different career or business opportunities in other fields as well.
Wishing you all a splendid and exponentially growing career journey ahead.

I am Anuja Sharma, presently pursuing a Fellow Programme in Management (FPM) from the Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India (EDII), Ahmedabad. I am pursuing my research in the field of social entrepreneurship. I have done my MBA specialising in finance and marketing from Gurukul Kangri Vishwavidhyala, Haridwar in the year 2021. I have done B.com(Hons) from Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University (BBAU), Lucknow. My interest lies in socialising with people who are involved in social activities. I have the skill to counsel a child to show them the right path by understanding the needs of an individual. Communication is also a positive factor, which I pursue and can teach others as well.



Great – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, website theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..